As a startup founder or entrepreneur, financial metrics and measurements are often a mystery, and rightfully so. With a focus on growth, product-market fit, and acquiring customers, it’s easy to overlook the importance of understanding the financial health of your business. One of the most critical financial metrics that every startup should understand is EBITDA. It’s a term that’s thrown around frequently in boardrooms and investor meetings, but what exactly does it mean, and why is it crucial for your startup? In this article, we will explore the concept of EBITDA in detail, explain why it’s important for startups, and provide an example to help clarify its significance.
What is EBITDA?
EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. It is a measure of a company’s operating performance that looks at the profitability of a business before the impact of financial decisions, accounting practices, and tax strategies. Essentially, EBITDA is a way to focus on the core operations of a company, removing the effects of financing and accounting decisions that can vary greatly across companies and industries.
In simpler terms, EBITDA shows the company’s ability to generate profits from its core operations, without factoring in how the company is financed, its tax obligations, or non-cash accounting items like depreciation and amortization.
Here’s the breakdown of the components that make up EBITDA:
- Earnings: Refers to the company’s net income or profit.
- Before Interest: Removes the effects of how the company is financed. Different companies may use debt or equity financing, and interest payments will affect their profitability, so this metric strips out interest expenses.
- Before Taxes: Taxes can differ based on the company’s location and tax strategy. By excluding taxes, EBITDA provides a clearer picture of operational performance across different regions and tax situations.
- Before Depreciation and Amortization: Depreciation and amortization are non-cash expenses related to the gradual write-off of tangible and intangible assets. By removing these, EBITDA allows for a focus on operational efficiency.
Why is EBITDA Important for Startups?
For a startup, EBITDA is a particularly important metric for several reasons. When you’re early in your entrepreneurial journey, profitability might not be your immediate focus—many startups are working to build their product, acquire customers, and scale. However, understanding EBITDA can help you assess your company’s core operations and present your startup in a better light to investors, stakeholders, and potential acquirers.
1. Assessing Operational Efficiency
EBITDA removes the impact of financial and accounting choices, giving you a clearer picture of how efficiently your company is running. By looking at EBITDA, you can determine whether your core business activities (e.g., sales, production, marketing, and delivery) are profitable. This helps you focus on improving your core operations, rather than getting distracted by non-operational factors like interest costs or tax strategies.
For example, if your startup is generating a solid EBITDA but still isn’t profitable, it could indicate that the issue lies in other areas of your business, such as excessive interest payments on debt or high taxes, rather than the product or service itself.
2. Attracting Investors and Partners
Investors and potential partners often prefer using EBITDA as a key performance indicator (KPI) to evaluate a company’s performance. Since EBITDA excludes non-operational factors, it provides a clear and standardized measure that makes it easier for investors to compare companies, regardless of their financing or accounting structures. EBITDA also shows investors how much money a company is making from its core business before any additional external costs are considered.
For example, if your startup is looking to raise Series A funding, investors will want to know how well your business is performing at its core. While net income is important, EBITDA allows investors to focus solely on the profitability of your business activities, which is particularly useful if you’re still in the growth phase and not yet showing significant net profits.
3. Valuation and Exit Strategy
When startups are preparing for an exit strategy—whether through acquisition or an initial public offering (IPO)—EBITDA is often a critical factor in the valuation process. Buyers and acquirers typically use a multiple of EBITDA (called the EBITDA multiple) to determine a startup’s value. The EBITDA multiple can vary widely depending on the industry, company growth rate, and market conditions, but it serves as a benchmark for startup valuations.
For example, if a startup has an EBITDA of $500,000 and the industry average EBITDA multiple is 5x, the company’s estimated value would be $2.5 million. This is a common method for valuing startups, especially in the tech and SaaS (Software as a Service) industries, where high growth potential is factored into the valuation.
4. Managing Cash Flow and Predictability
EBITDA is a helpful metric for forecasting cash flow and identifying potential cash shortages. By isolating operating income from non-cash and non-operational expenses, EBITDA can give you a sense of how much cash the business is generating from its core activities. This is critical for planning and budgeting purposes. Since startups often face cash flow challenges as they scale, understanding your EBITDA can help you make more informed decisions about spending, investment, and growth strategies.
If your EBITDA is healthy but your cash flow is struggling, it could signal issues with working capital, such as delays in receivables or high inventory levels. In contrast, strong EBITDA alongside healthy cash flow can indicate that the business is running smoothly and efficiently.
Example of EBITDA Calculation
Let’s break down EBITDA with a practical example. Suppose you’re the founder of a tech startup, and you’re looking to calculate your EBITDA for the past year. Your income statement shows the following details:
- Net Income (Earnings): $300,000
- Interest Expenses: $50,000
- Tax Expenses: $70,000
- Depreciation and Amortization: $40,000
To calculate EBITDA, we start with the net income and then add back interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
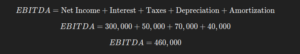
In this example, the startup’s EBITDA is $460,000, which shows the company is generating $460,000 from its core operations before accounting for interest, taxes, and depreciation.
Limitations of EBITDA
While EBITDA is a valuable tool for understanding a company’s operational performance, it does have limitations. For instance, EBITDA does not account for capital expenditures (CapEx), which are important for growth-oriented startups. It also ignores the costs of acquiring assets and paying down debt. Therefore, EBITDA should never be viewed in isolation; it must be used in conjunction with other financial metrics such as net income, free cash flow, and debt-to-equity ratio to provide a comprehensive view of a startup’s financial health.
EBITDA is a powerful metric for evaluating a startup’s core operational performance and plays a significant role in attracting investors, securing funding, and planning for an exit. Understanding EBITDA helps you gauge how efficiently your business is running and offers insights into areas where you might need to improve, whether it’s scaling operations, managing cash flow, or refining your business model.
As a startup founder, being familiar with EBITDA and how it impacts your business can give you a competitive edge when negotiating with investors, partners, or acquirers. While it’s important to understand the calculation and interpretation of EBITDA, it’s equally crucial to use it alongside other metrics to ensure that you’re making well-rounded decisions that foster long-term growth and success.
By grasping the significance of EBITDA and applying it strategically, startups can navigate the complex world of business finance with greater confidence and clarity.




